What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network and how does it work?
Bitcoin (BTC) has marked a before and after in the financial world; however, it faces a major challenge: “scalability,” which affects transaction times and costs. This is where the Lightning Network comes into play, a second-layer solution designed to make Bitcoin payments almost instantaneous and with nearly nonexistent fees.
In this blog, we will explore the Bitcoin Lightning Network, its operation, and its significance as one of the most critical innovations in the crypto ecosystem. If you’ve ever wondered how BTC can compete with traditional payment systems like Visa or Mastercard regarding speed and cost, you’ll find all the answers here.
What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network, also known as LN, is a second-layer solution built on top of the original Bitcoin blockchain. This protocol was introduced by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja in a publication released in January 2016.
It allows sending and receiving BTC quickly and securely. Its most notable features are its near-instant transaction time and almost zero fees.
It’s worth pausing here to explain what a second-layer off-chain solution is. Basically, it’s a second blockchain network built on top of a base blockchain or layer 1. Additionally, second-layer solutions inherit the security of the base blockchain.

How many transactions per second can the Bitcoin Lightning Network handle?
It’s no secret that Bitcoin (BTC) has the inability to execute a high volume of transactions in a short period. This is mainly because a block is added to the Bitcoin network every ten minutes, limiting the block size.
For this reason, Bitcoin can only handle between five and seven transactions per second, while Visa can handle over 20,000 in the same amount of time. The Lightning Network protocol solves this problem, theoretically handling millions of transactions per second.
How does the Bitcoin Lightning Network work?
Okay, the LN’s workings are a bit complicated and different from traditional blockchains. So, at Bitsa, we will do our best to explain this complicated process, which has made the Bitcoin Lightning Network the favorite protocol of Bitcoiners for microtransactions.
The Lightning Network uses Smart Contracts to establish off-chain payment channels between users who want to transact in LN. Once these payment channels are established, funds can be transferred between them almost instantaneously.
These payment channels are essential to the network’s operation, enabling low costs and short wait times.
We know this wasn’t clear, so let’s explain better with a step-by-step example:
- Opening a payment channel: Two users (e.g., Alice and Carol) lock a certain amount of Bitcoin in a smart contract on the Bitcoin blockchain. This creates a private channel between them, which they can use to exchange payments without registering each transaction on the main blockchain.
- Exchanging payments within the channel: Once the channel is open, Juan and Andrea can send Bitcoin to each other as many times as they want without touching the Bitcoin blockchain. Only a balance within the channel is updated, ensuring everyone gets their fair share of the funds.
- Closing the channel and settling on the blockchain: When they no longer want to use the channel, they can close it. At that moment, the final balance is recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain, reflecting the exact amount of BTC each one owns.
- Using intermediate nodes: The most interesting part is that you don’t need to open a channel with everyone you want to make payments with. The Lightning Network allows routing payments through intermediate nodes. If Juan wants to pay Andrea but doesn’t have a direct channel with her, the network finds a route using other open channels (e.g., through Bob). This process happens in seconds and without traditional intermediaries.
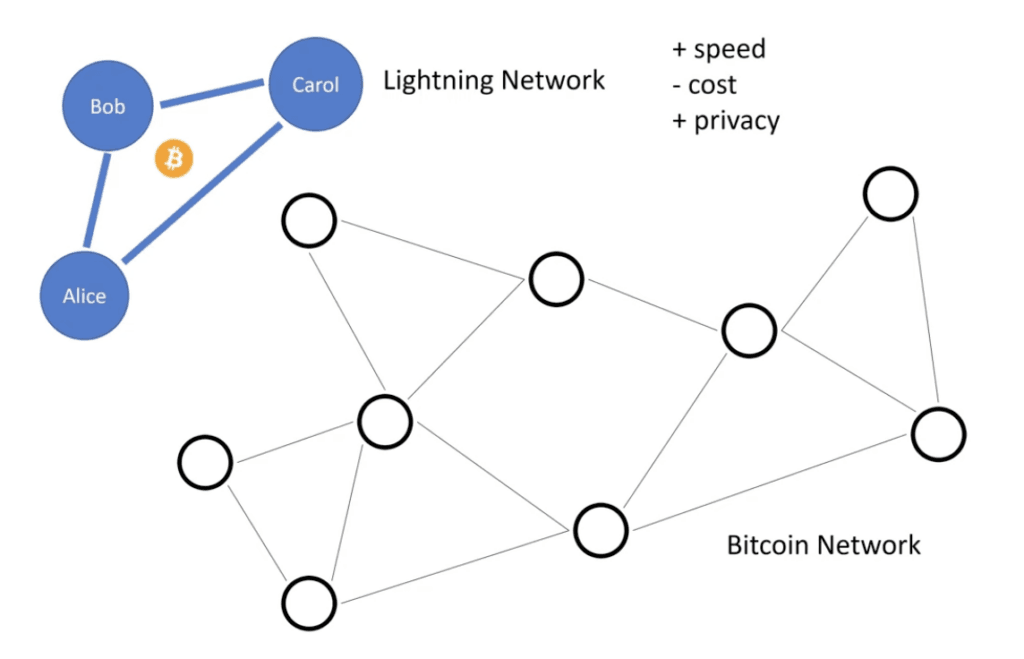
What are the payment channels in the Lightning Network?
This brings us to the next concept: understanding the complicated but very secure process by which the Lightning Network operates.
Basically, they’re like a type of “shared account” between two people. Funds can move freely until the channel is closed and the final balance is settled on the main blockchain.
But, as mentioned earlier, you don’t need to open a payment channel with everyone or every store you will transact BTC with. Instead, the network functions as an interconnected system of channels where payments can be routed through third parties securely and without trust.
It’s also important to note that if Andrea disconnects and Juan keeps operating, the BTC balance in the channel won’t be indefinitely trapped in it. Instead, users can unilaterally close the channels within the Lightning Network smart contract mechanisms.
When a payment channel is closed after an indefinite number of exchanges, the final funds for each party are recorded on the main Bitcoin blockchain.
Security in the Lightning Network: How secure is it?
As mentioned, one benefit of building layer 2 is that it inherits the security of the base blockchain, in this case, the most secure blockchain of all: Bitcoin.
However, the security systems within second-layer networks can vary from those of their base blockchain. This is the case with LN. The Lightning Network relies on payment channels that function with smart contracts and cryptographic signatures. Each channel is a kind of “agreement” between two parties that ensures funds can only move under certain pre-established conditions.

Payments in the network are made off the main Bitcoin chain, but each transaction is backed by the blockchain. If something goes wrong, either party can close the channel and settle the balance on the main Bitcoin network, ensuring the funds aren’t lost.
One key security mechanism in the Lightning Network is the “penalty mechanism.” If a user tries to cheat by broadcasting an old state of the channel (to recover an older balance and benefit from it), the network allows the other party to claim all the funds as a punishment. This incentive discourages attackers and protects honest users.
Additionally, payments on the network are protected with HTLCs (Hashed Time-Locked Contracts), a type of smart contract that ensures funds are only released if certain conditions are met within a set time. If these conditions aren’t met, the transaction is automatically reversed, preventing losses.
The Lightning Network is a fast, efficient, and highly secure alternative for users making small and frequent payments. However, those handling large volumes of Bitcoin should take additional precautions.
Current limitations of the Lightning Network
- Unlike traditional blockchain transactions, transactions in the Lightning Network can only be made between users with an active payment channel.
- The network is still in development, and its creators recommend not using it for high-volume operations due to its current limitations.
- The liquidity of the channels is limited by the funds locked by their participants, which can restrict high-value payments.
- Users must divide their funds between the main blockchain and the Lightning Network, which may affect capital availability for certain operations.

Real-world use cases of the Lightning Network
- Micropayments: Allows small BTC transactions, even fractional euros, without incurring high fees.
- E-commerce: Facilitates instant payments in online stores without waiting for confirmations on the main Bitcoin chain.
- Payments in physical stores: Enables fast payments in physical establishments using QR codes.
- International remittances: Offers a fast and economical alternative for sending remittances worldwide, avoiding high fees from traditional services.
- Tips and rewards: This feature allows users to instantly send tips to content creators, artists, or service workers at negligible cost.
Given these use cases, the adoption of the Lightning Network by large companies is still growing, but several major companies and platforms have already implemented it to enable fast and cost-effective Bitcoin payments.
- Shopify: It has an agreement with Strike to receive payments through the Lightning Network in BTC.
- McDonald’s: Accepts Bitcoin in El Salvador through the Lightning Network.
Bitsa: Connect your cryptos to real life
Cryptocurrencies are becoming an increasingly essential part of our daily lives. With Bitsa cards, you can use up to 8 cards simultaneously, recharged with your favorite crypto.
Living with your cryptocurrencies today is a reality; you can do it your way. Discover more.